The Structure of the Nucleus Can Be Described as
It is responsible for controlling all activities of the cell. Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus which means the cellâ s DNA is surrounded by a membrane.
Nucleus Definition Structure Parts Functions Diagram
The ratio of the size of the nucleus to the electron cloud is 1100000.
. Protons and neutrons in orbit about a nucleus of electrons. The nucleus has been clearly explained as a membrane-bound structure that comprises the genetic material of a cell. Structure and Organization of the Nucleus As the organelle that contains the genetic material of a cell the nucleus can be described as the command center.
The two shells that contain the electrons make up the electron cloud. O Is where DNA is organized into discrete units called chromosomes Nuclear envelope enclosed the nucleus separating its contents from the cytoplasm. This section gives focus to the structure of the cell.
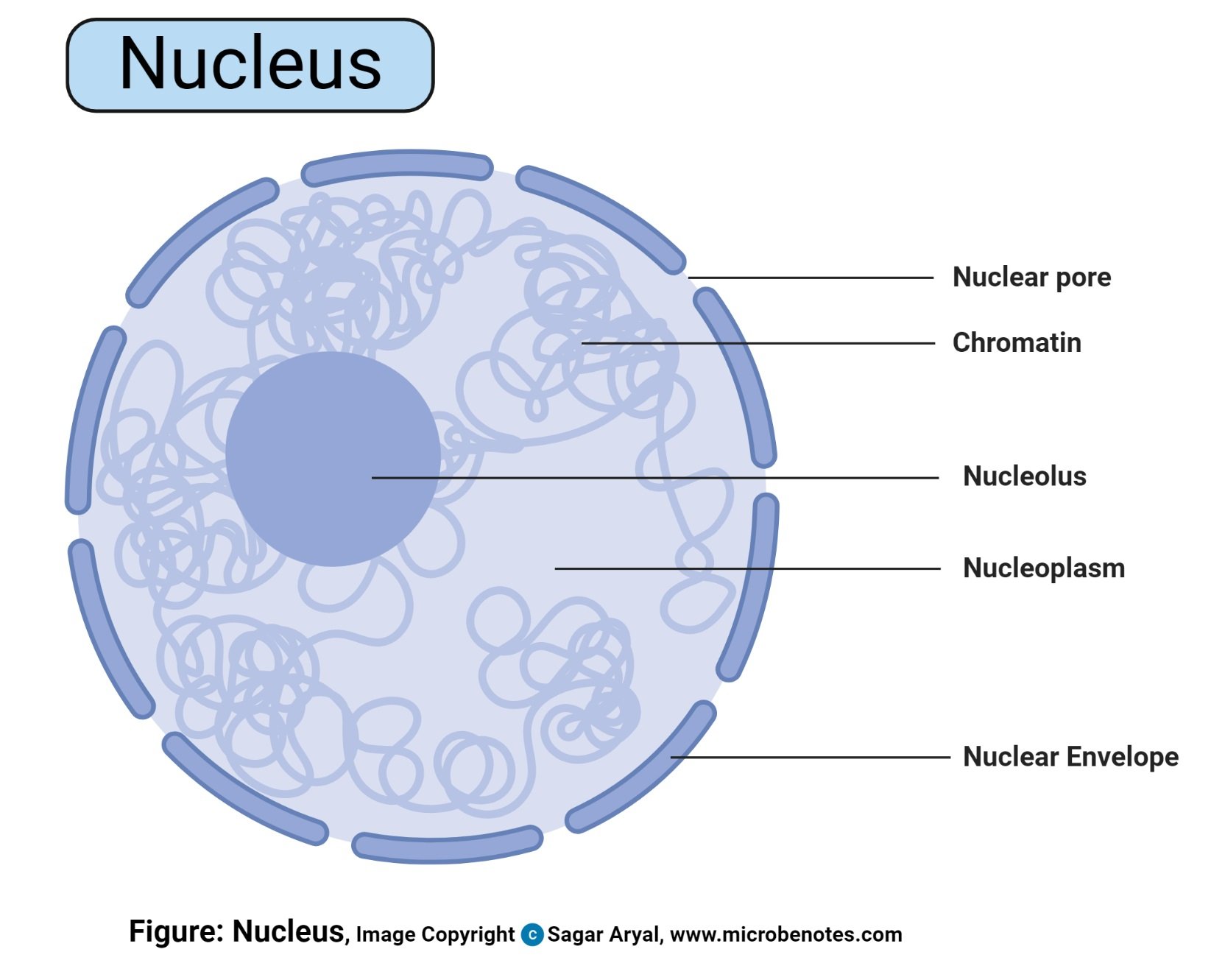
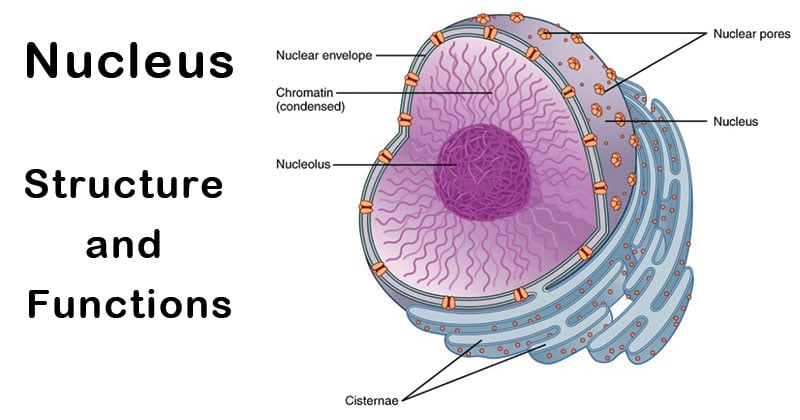
And contains a nuclear membrane chromosomes nucleolus and nucleoplasm. In an animal cell the nucleus is located in the central place of the cell. Function The key function of the nucleus is to control cell growth and multiplication.
The structure of the nucleus can be described as enclosed in a cell membrane enclosed in a nuclear envelope composed of cytoplasm composed of cytoplasmic organelles. First and foremost it is possible to duplicate ones DNA in the nucleus. Structure of the Nucleus As the organelle that contains the genetic material of a cell the nucleus can be referred to as the command center.
It contains all of the cellâ s genetic material. There are exceptions which will be discussed later. The structure of a nucleus encompasses nuclear membrane nucleoplasm chromosomes and nucleolus.
Nucleus is considered as the controlling centre of the cell. Nucleus contains most of the genes in the eukaryotic cell some genes are located in mitochondria and chloroplasats. White blood cells are an illustration one with lobed nucleus.
The ovum egg cell in the animals and the plants. The nucleus structure is unique. TorF the structure of the nucleus can be described as being enclosed in a nuclear envelope.
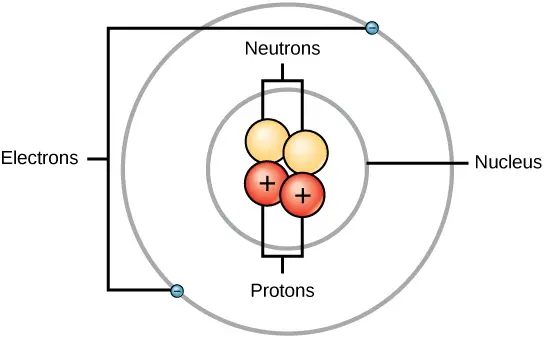
As such the nucleus consists of a number of structured elements that allow it to perform its functions. So there is a massive nuclear core and around this massive core the electrons are presumed to whizz about to orbit in a generally predictable way. The diagram below cuts an atom in half so we can see how it is arranged.
In general the nucleus has a spherical shape. The nuclei of some atoms are spherical while others are stretched or flattened into deformed shapes. Neutrons in orbit about a nucleus of protons bound to electrons.
Electrons and neutrons in orbit about a nucleus of protons. This section gives focus to the structure of the cell. To then allow the nucleus to be the peak of sonority Consonants Cs being less sonorant flank the nucleus in the onset and coda positions.
The binding energy of a nucleus is the energy holding a nucleus together. How structure function of nucleus can be described. The structure of an atom is best described as.
Usu View the full answer Transcribed image text. Nucleus occupies an extremely small volume inside the atom. At one extreme the nucleus has been proposed to have its own nucleoskeleton and distinct organelles.
Structure and Organization of the Nucleus As the organelle that contains the genetic material of a cell the nucleus can be described as the command center of a cell. The nucleus is a sphere-shaped organelle found in eukaryotic cells. As shown in Fig.
O About 5 micrometers um in diameter. 2-4 this energy varies from nucleus to nucleus and increases as A increases. Nerve processes exist as either dendrites or axons.
Science Join the conversation. As such the nucleus includes a variety of structured aspects that permit it to perform its functions. According to the SSP the nucleus is the peak of sonority.
It is the command center of a eukaryotic cell and is usually the most notable cell organelle in both size and function. With increasing degrees of sophistication the electrons are confined to various energy levels shells in other words and within the shell there are prescribed sets of orbitals. The cell nucleus is a membrane-bound structure that contains a cells hereditary information and controls its growth and reproduction.
Likewise in the plant cell the nucleus is located more on the periphery due to the large water-filled vacuole in the center of the cell. The nucleus is an organelle that consists of the genetic information for that organism. The structure of a neuron can be described as a cell body with nerve processes that transmit signals from one neuron to another.
What is the Nucleus. The protons green and neutrons yellow can be seen in the nucleus. The structure and functional organization of the nucleus remains a subject of energetic debate.
Nucleolus In the nucleus there is a thick non-membrane structure that is made up of RNA as well as proteins referred to as the nucleolus. It contains the genetic material of the cell in the form of nucleic acids. That is the description of an atom the basic unit of matter.
First described by Brown in 1831 the cell nucleus is one of the best known but least understood of cellular organelles. It is not just a storage compartment for DNA but also happens to be the home of some important cellular processes. It Is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells that contains the chromosomes as well as bits of RNA.
The nucleus could be described as bilobed multi-lobed or tri-lobed based on the amount of lobes. The nucleus is usually filled with a vowel V because vowels are the most sonorous sounds. As such the nucleus consists of a number of structured elements that allow it to perform its functions.
The cell body of the neuron contains the nucleus.
Nucleus Definition Structure Function Cellular Vs Atomic Nuclei

Describe The Structure Of Nucleus

Nucleus Definition Structure Composition Functions Worksheet

The Structure And Function Of Nucleus Structure And Function Nuclear Membrane Eukaryotic Cell
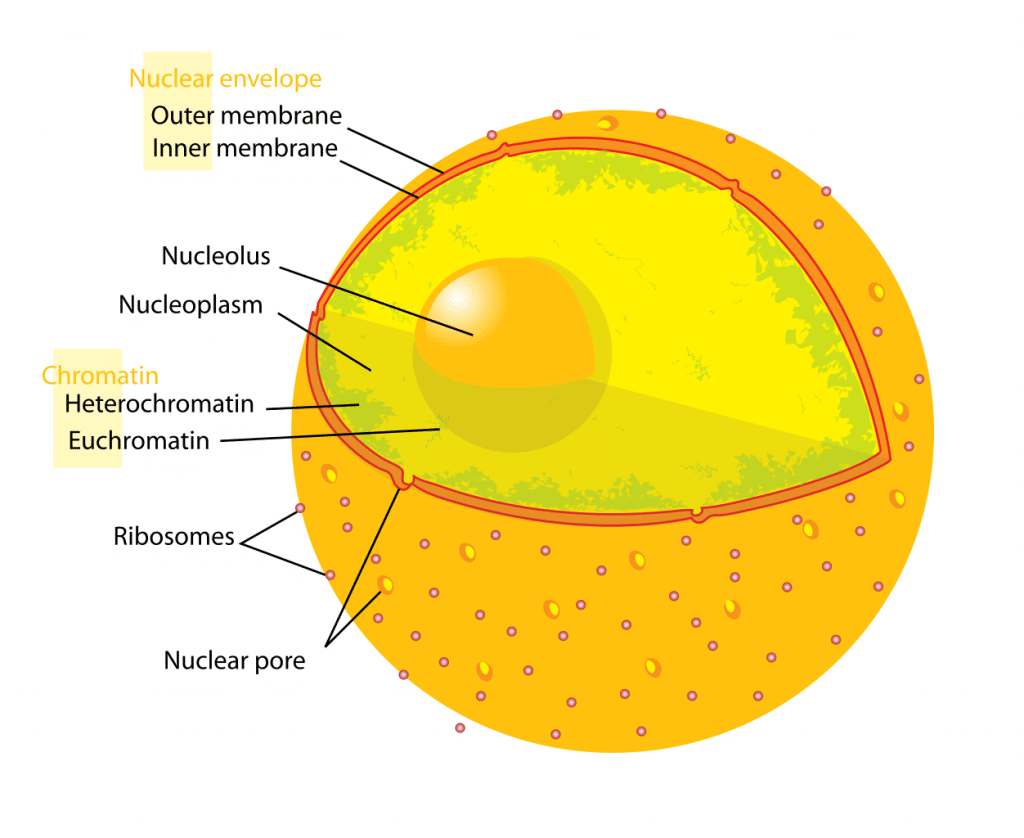
Nucleus Structure Function Euchromatin Teachmephysiology
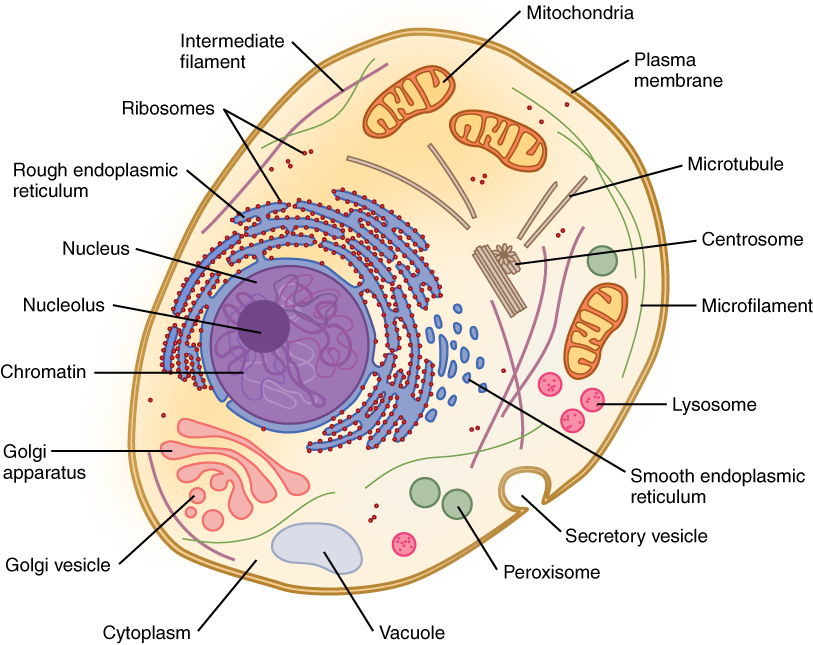
The Nucleus And Cytoplasm Anatomy And Physiology
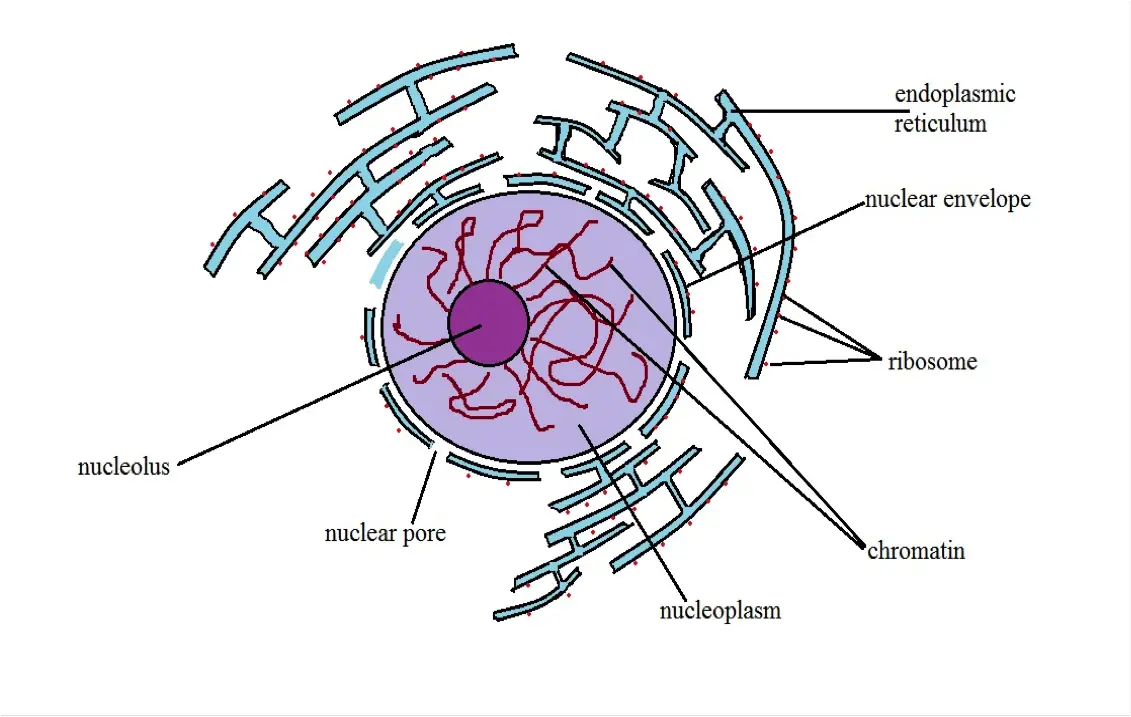
Nucleus Definition Structure Function Cellular Vs Atomic Nuclei

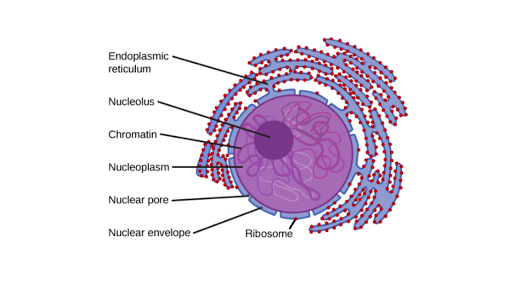
Nucleus And Ribosomes Article Khan Academy
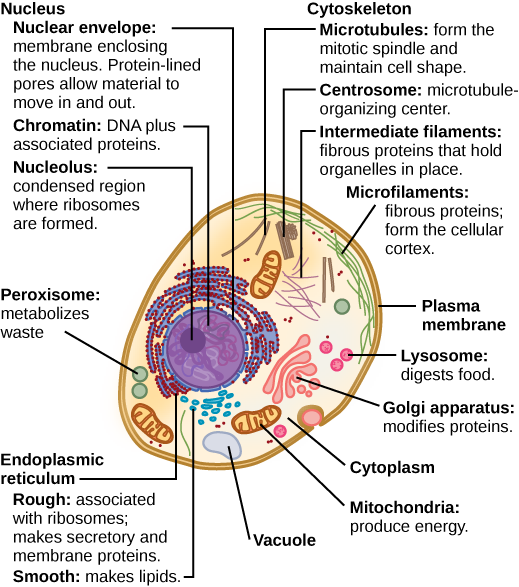

Eukaryotic Cells Boundless Biology

Nucleus Structure Function Euchromatin Teachmephysiology

Atom Rutherford S Nuclear Model Britannica
Nucleus Cell Nucleus Nucleus Structure And Functions

Nucleus Structure And Functions A Level Biology Revision Notes


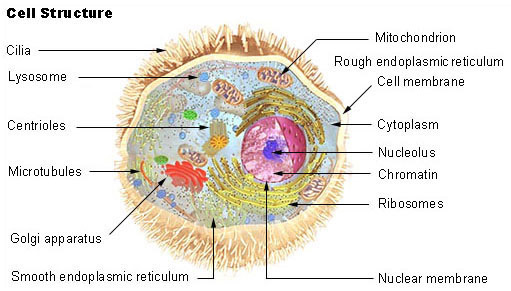
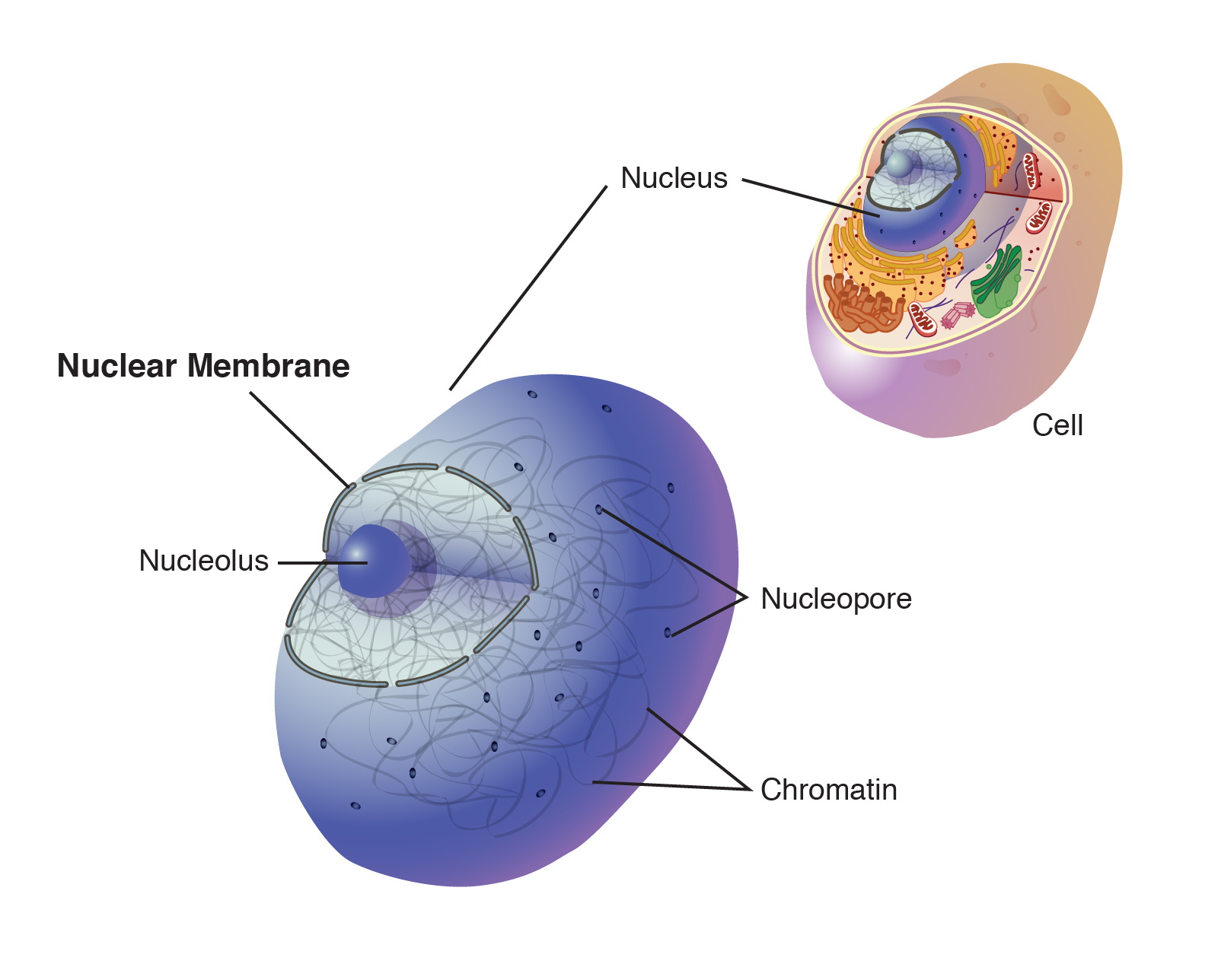
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/nucleolus/cpz4j9r1x6VuyNmmbgdA_Nucleolus.png)
Comments
Post a Comment